
There are many different types, sizes, and shapes of robots. They operate in operating rooms these days, backflip through obstacle courses, explore space, and go down the uncanny valley. Furthermore, robot intelligence and machine learning are growing, which means that robots will only get more advanced. These programmable technologies are altering society as a whole as they discover new methods to automate routine operations and jobs across a range of sectors. These are a few distinct kinds of robots that are pushing the boundaries of what was previously believed to be achievable for computerized devices.
WHAT IS A ROBOT?
A robot is a machine that can be programmed to carry out an action with little assistance from a person. They are usually made to quickly and accurately perform hazardous or repetitive tasks in place of human labour.
TYPES OF ROBOTS
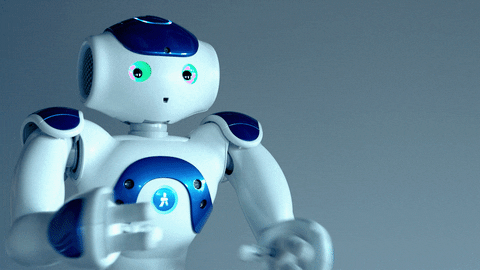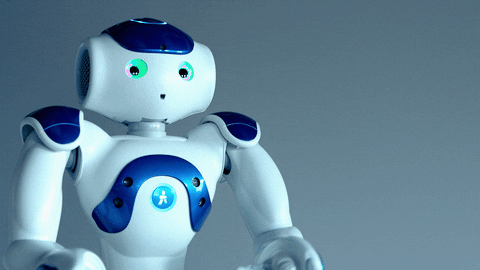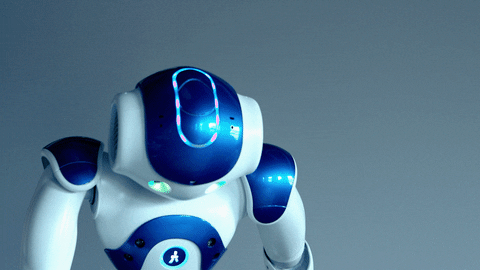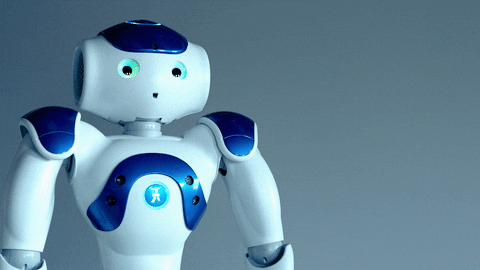
HUMANOID ROBOTS [Ref]
Robots designed to mimic humans in both form and function are called humanoid robots. Actuators are used by engineers to mimic the movement of muscles and joints. A range of sensors, including those with computer vision and haptic feedback, are used to sense their environment. Artificial intelligence algorithms, such as machine learning and speech recognition, are used to enable autonomous interpretation and interaction with their environment. Humanoids are mostly being produced for research and professional services applications, while the majority of models are still in the prototype stage.

INDUSTRIAL ROBOTS
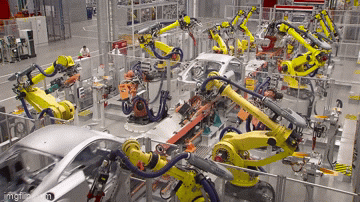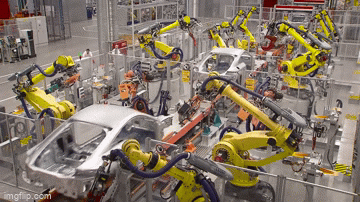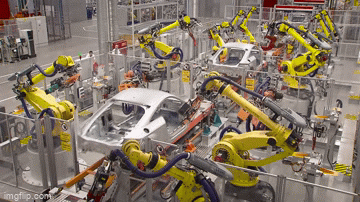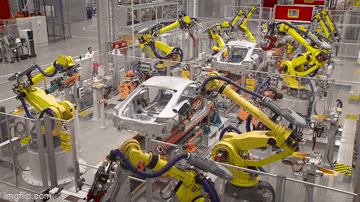
Industrial robots are large, powerful devices that greatly automate production operations. These large devices, which are made up of at least one programmed manipulator that resembles an arm, operate precisely and steadily from a stationary position. They may move in three or more dimensions. Industrial robots are typically integrated into assembly lines in warehouses and factories to handle materials, weld, palletize, inspect, and test goods. Currently, the global count of industrial robots exceeds 3 million.
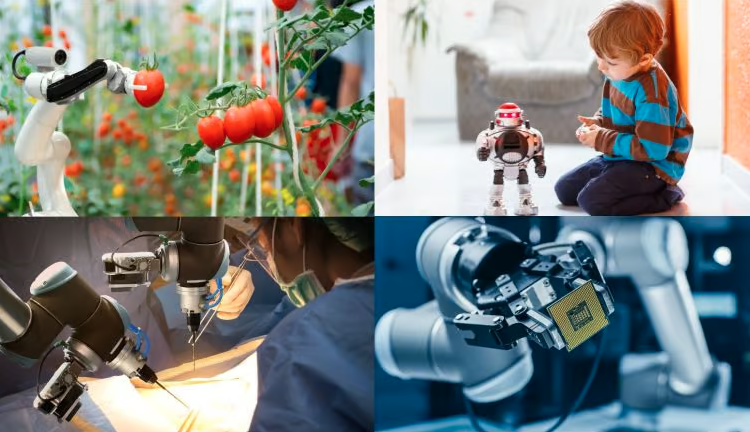
SOCIAL ROBOTS
Social robots are AI-driven friends designed to engage with people. When interacting with a user, these robo-buddies imitate human-like actions and facial expressions to show that they understand. To process social cues associated with touch, sound, and vision, they rely on sensors, cameras, microphones, and computer vision. Social robots are frequently employed to assist with early childhood development, particularly in the context of autism therapy and social-emotional learning, as well as to provide companionship for elderly people who are ageing in place or astronauts who are in space.
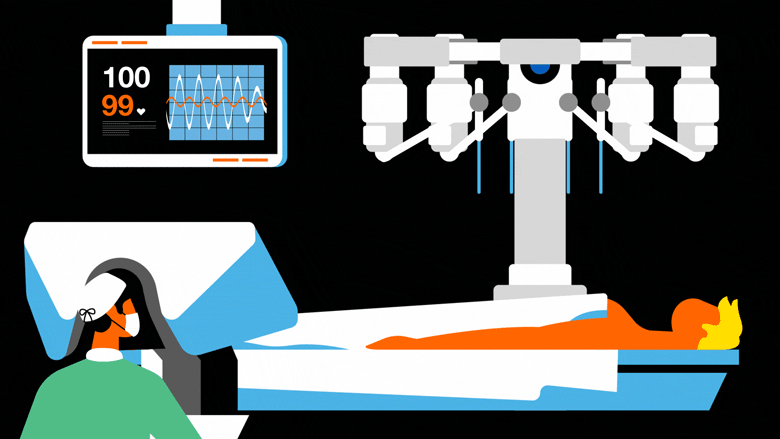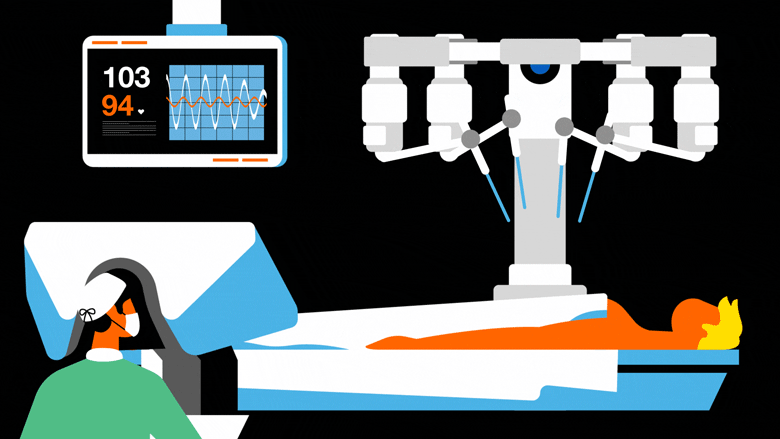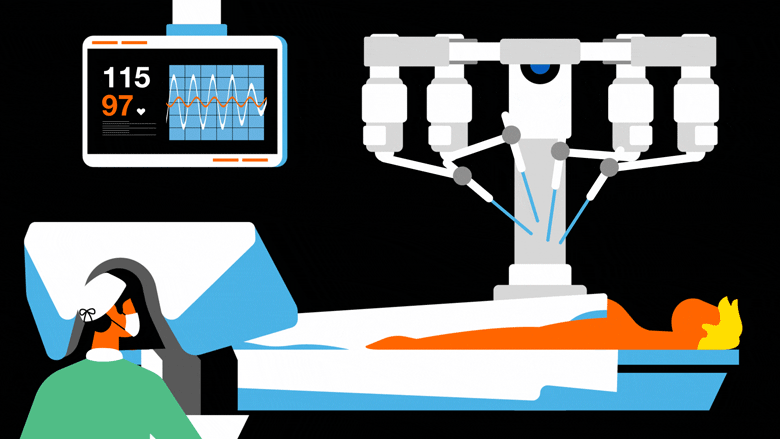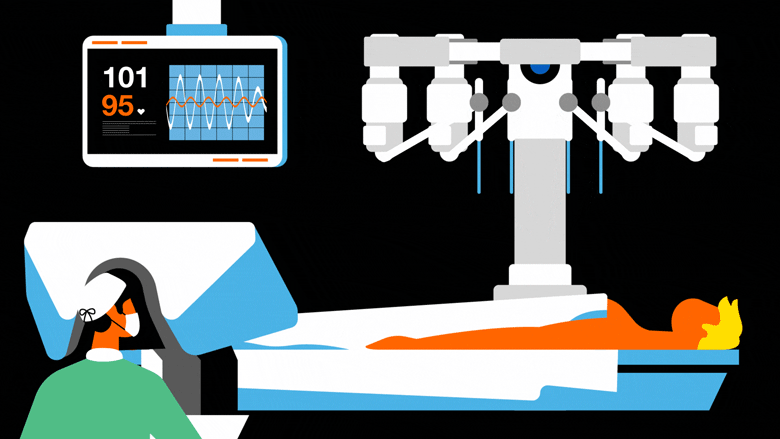
MEDICAL ROBOTS
Medical robots are tools and systems that assist medical practitioners in treating patients and optimising hospital operations. These high-precision devices, which provide a broad range of applications from diagnostics and patient care to surgery and rehabilitation, are frequently outfitted with sensors, imaging technologies, and telemanipulators in an effort to enhance patient outcomes and decrease human error. Robotic prostheses restore function by transmitting brainwaves to an artificial limb, while surgical robots allow for dexterity beyond human skills and minimally invasive procedures.
SERVICE ROBOTS
Service robots are designed to assist humans in various personal and professional settings. They are usually assigned tasks that are monotonous, unclean, repetitive, or hazardous, and are utilized outside of industrial environments to streamline everyday activities. These robots can handle household chores, support elderly individuals in maintaining their independence, greet hotel guests, or even prepare burgers and pies in a restaurant kitchen.

COBOTS
Cobots, which are a combination of “collaborative” and “robot,” are machines specifically created to operate alongside humans in a shared workspace. These robots are equipped with advanced sensors and safety features that enable them to perform tasks near humans without requiring physical barriers. By automating monotonous, repetitive, and physically demanding tasks, cobots significantly enhance productivity, allowing their human counterparts to concentrate on more valuable aspects of their work.
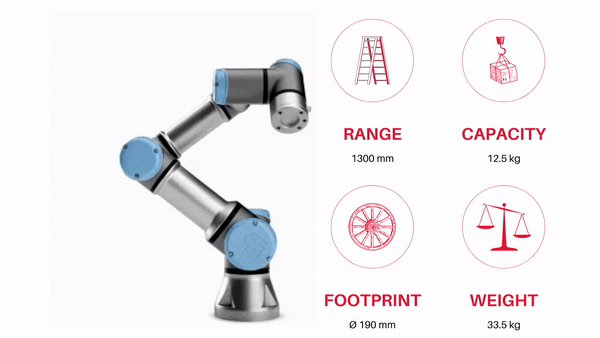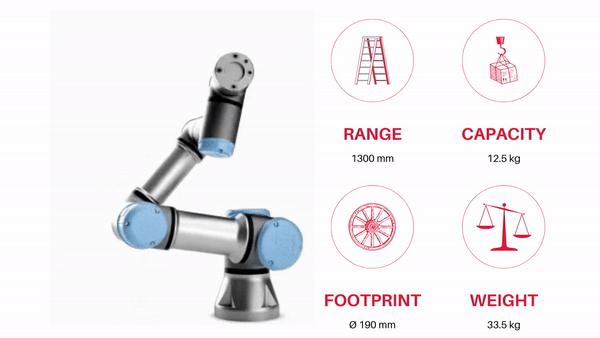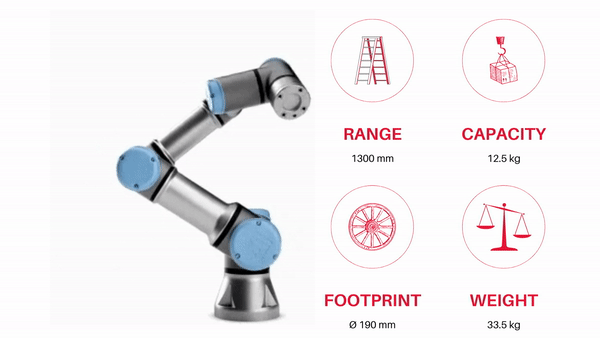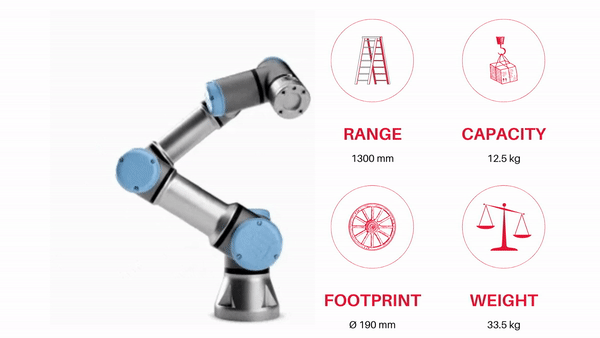
SPACE ROBOTS
Space robots refer to unmanned vehicles that are deployed beyond Earth’s atmosphere with the primary objective of exploring space. These vehicles, including rovers, landers, and orbiters, carry out various tasks in outer space, such as capturing images, collecting samples, and conducting experiments. The data they gather is relayed in real-time to mission control centers on Earth or to nearby manned spacecraft. Space robots can operate autonomously, semi-autonomously, or under remote control. They provide a safer and more cost-effective alternative to human-led space missions.

EDUCATIONAL ROBOTS
Educational robots are robotic tools that serve as teaching aids to enrich the learning process in educational environments. These robots provide tangible platforms for experimentation, fostering more interactive classrooms with hands-on activities and engaging lessons. They come in various forms, including virtual reality headset systems, simulators, and droids, and are highly programmable. These robots are designed with user-friendly interfaces that cater to younger audiences. Certain humanoid models even act as teaching assistants, personal tutors, small group leaders, and classroom peers, equipped with sensors that can perceive emotions to aid students in developing their social skills.
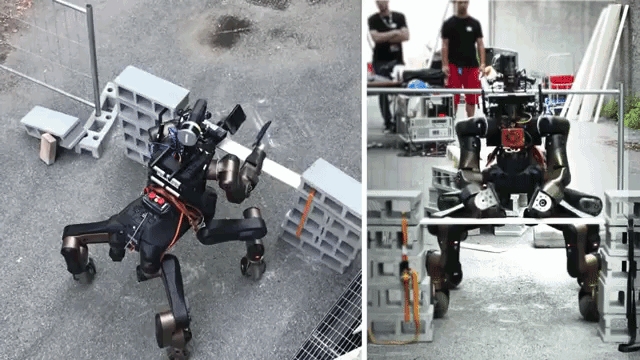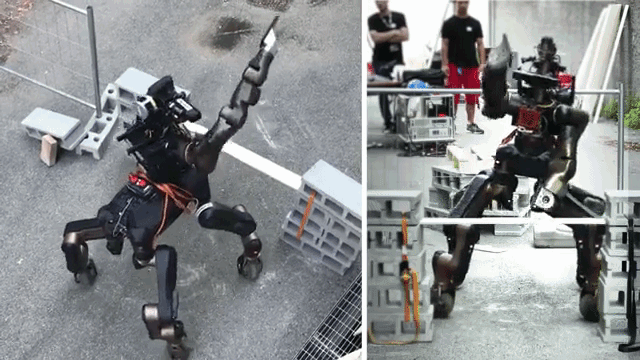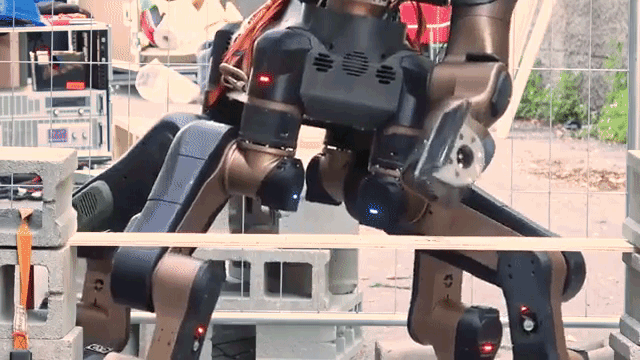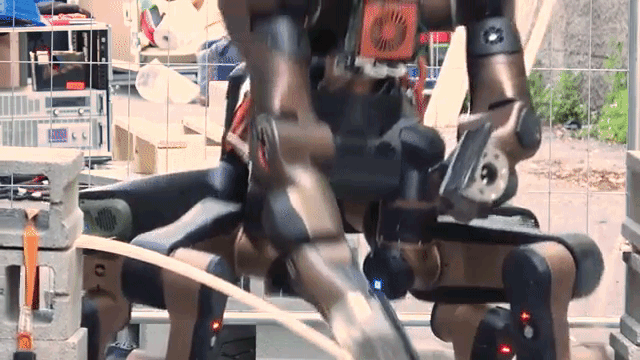
RESCUE ROBOTS
Rescue robots are robotic tools that provide assistance to response teams during search and rescue missions. Their primary purpose is to navigate hazardous environments and reach areas that may be unsafe for humans. These versatile machines are capable of flying, swimming, and crawling through earthquake rubble, as well as extinguishing fires. Equipped with sensors, they can assess treacherous terrains, utilize GPS to map and search large areas, and employ cameras and microphones to locate trapped individuals. Additionally, rescue robots feature vertical take-off and landing capabilities, as well as grippers to deliver essential supplies like food and medical aid.
AGRICULTURAL ROBOTS
Agricultural robots, also known as agribots, are a category of field robots designed to automate labor-intensive and repetitive tasks in the agricultural sector. These advanced farming machines are used in various areas such as livestock farming, aquaculture fisheries, and forest management. They offer a data-driven approach to improve industry practices like harvesting, irrigation, seeding, and environmental monitoring, depending on their specific functions. As the demand for food increases and labor shortages become more prevalent, agribots are playing a significant role in reducing costs, conserving resources, minimizing chemical usage, and increasing crop yields.

EXOSKELETONS
Exoskeletons are wearable devices created to enhance mobility by working in collaboration with the user. These mechanical structures, equipped with motor assistance, offer ergonomic support and help prevent injuries. Robotic prosthetic devices, whether utilized in industrial and defense settings or for patient rehabilitation in healthcare centers, can provide assistance in tasks such as heavy lifting, prolonged squatting, and load transportation.

AQUATIC ROBOTS
Aquatic robots undertake various tasks in marine environments. Whether they glide across the ocean’s surface or dive underwater, these unmanned vehicles operate in different modes, including autonomous, remote-controlled, or a combination of both. They are primarily employed in ocean exploration. Equipped with sensors, propulsion systems, and arm-like manipulators, these robots are capable of studying marine wildlife and habitats. They also play a crucial role in the maintenance of underwater structures such as pipelines and offshore platforms.
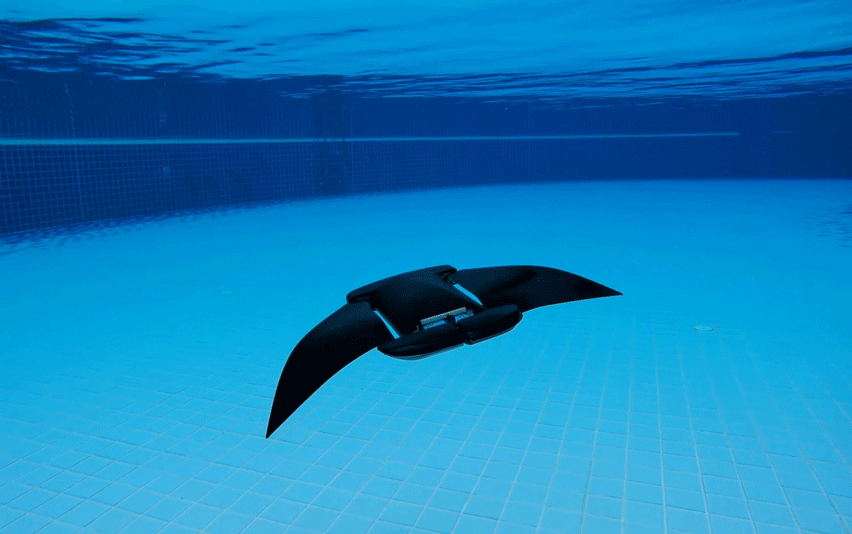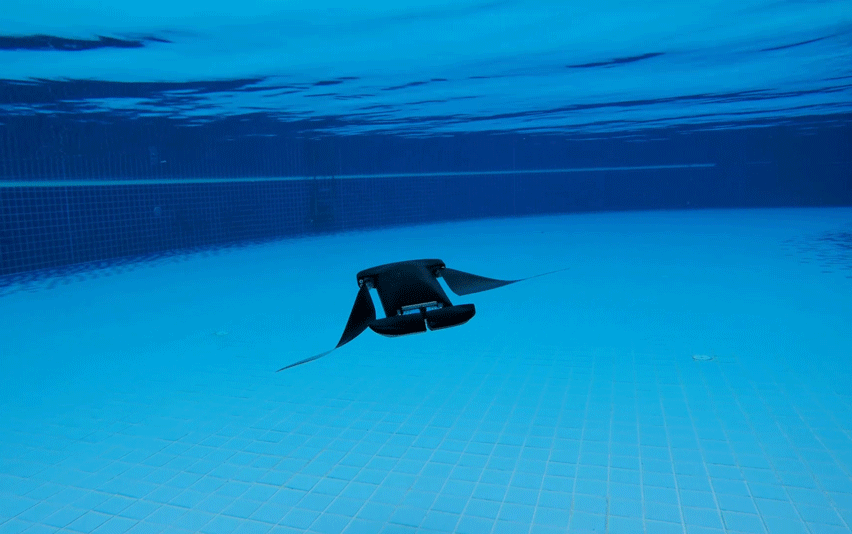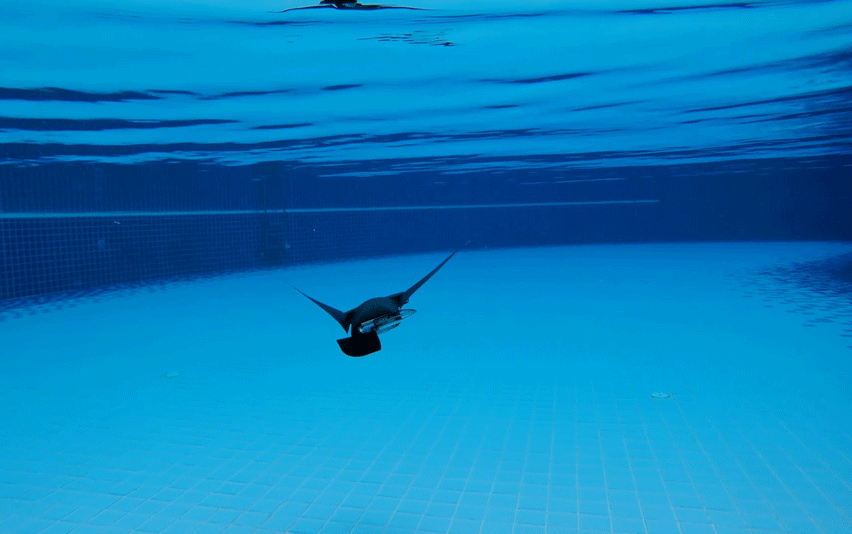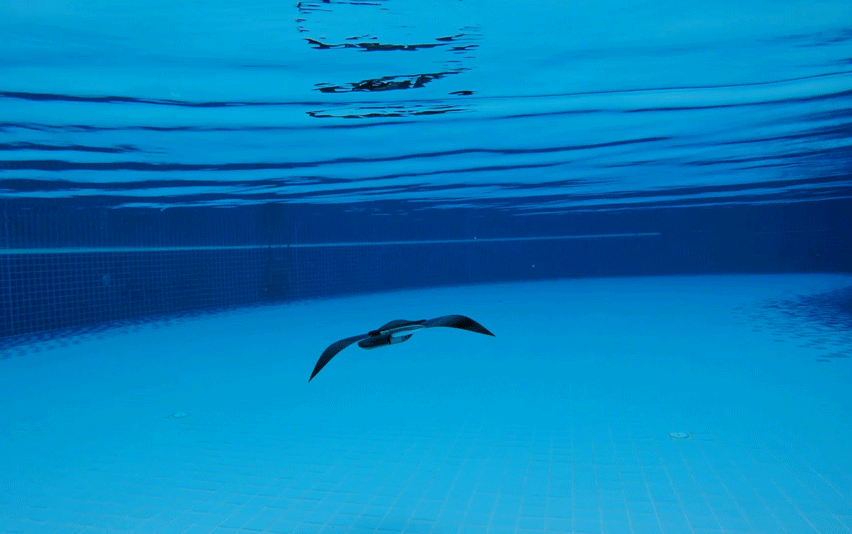
NANOROBOTS
Nanorobots are minuscule machines engineered to function at the nanoscale. These robots are constructed by assembling individual atoms using a combination of organic and artificial materials, including DNA molecules, peptides, silicone, and graphene. Generally, they have dimensions ranging from 50 to 100 nanometers, with one nanometer being equivalent to one billionth of a meter. Nanorobots hold immense promise in fields such as medicine, where they can be utilized for precise drug delivery, as well as in environmental cleanup efforts, where they can help remediate pollutants with targeted precision.

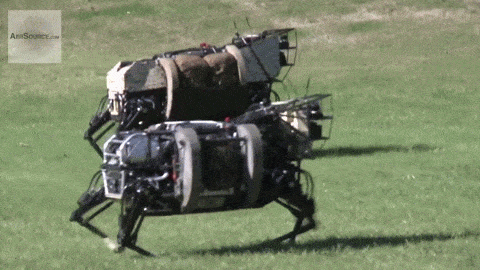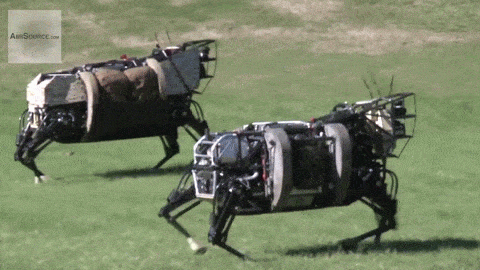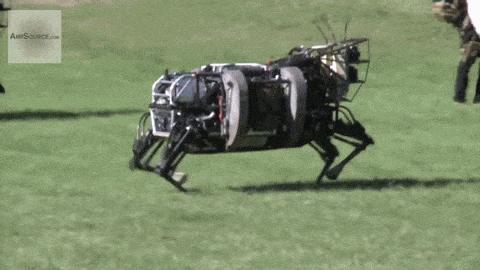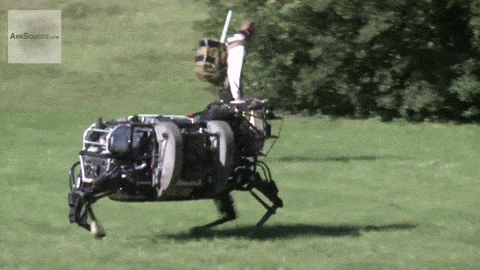
MILITARY ROBOTS
Military robots are unmanned robotic systems utilized for various military purposes. These machines, fitted with sensors, weapons, and communication systems, play a crucial role in modern warfare. They carry out targeted attacks and bolster intelligence capabilities, encompassing tasks such as reconnaissance, surveillance, and logistics support. By reducing the risk to human soldiers, military robots have become integral to military operations. Examples of such robots currently being developed include drones, tanks, minefield-clearing bots, mechanical guard dogs, and automated snipers.
Related Topics:
- AI Applications in Robot Technology
- How to write a paper using ChatGPT and Quillbot software?
- What is Artificial Intelligence (AI) or Deep Learning or Machine Learning?
- Top Agriculture Drones Using AI
- How to use free ChatGPT in an unauthorized country?
- Sophia Robot like a Human
- 25 Top Artificial Intelligence (AI) Apps
- Top 10 Free Video Editor Tools 2023
- The Impact of AI Applications in Medical, Industry, and Marketing
- Master/PhD Scholarships 2024 for International Students
- Bing Image Creator Free, AI art just in seconds
